Experience and expertise
Have you ever wondered what makes your experts—your top performers—so effective? What sets them apart from average performers? Experts possess highly organized mental models derived from extensive experience. This enables them to quickly comprehend and solve complex problems (Hoffman et al., 2013).
They excel in two key areas:
- They can handle familiar situations quickly and effortlessly-this is called “automaticity”.
- They are also great at dealing with new or tricky situations- this is called “flexibility.”
This combination forms the foundation of expertise. Experience shapes the mind, developing both automaticity and flexibility by building a large collection of mental models for common situations and teaching how to recognize important details in complex scenarios.
SkillGym’s mission is to create scenarios that empower employees to think and perform at the level of the company’s top achievers
Scenarios Creation
The first step to build your SkillGym scenario is to fill the Brief in.
In SkillGym’s universe, this step is crucial because when you define the scenario’s key elements and your best practice—setting the highest performance level—the role-play will transfer that knowledge to all users through practice.
Methodologically, in the literature, the step number one in creating an accelerated expertise training is the Cognitive Task Analysis (CTA): a broad family of research methods aimed at eliciting, unpacking, and representing knowledge (Klein & Militello, 2001). CTA seeks to understand an expert’s thought processes in great depth to teach them to others. There are over 100 different CTA methods documented in the literature.
While the Brief approach has its roots in CTA methodology, it has been adapted to accommodate the product’s specificities and organizational needs. The resulting method is a proprietary blend of suitable CTA techniques with specific modifications, rather than adhering to any single standardized CTA technique.
SkillGym’s Brief is designed to extract only the strictly necessary information from the client’s Subject Matter Experts. The remaining information needed to create a simulator is then derived by AI using a deductive method. This approach offers several advantages: it facilitates information elicitation from the client, speeds up and simplifies the process, and maintains the integrity of the elicited mental model.
The importance of flexibility
Now, let’s continue exploring the SkillGym method to understand its design and why it is considered highly effective according to the literature. In the discussion about the requirements for rapidized training, Hoffman et al., (2014) use the merge of two theories:
- Cognitive Flexibility Theory (CFT) (Spiro et al., 2013)
- Cognitive Transformation Theory (CTT) (Klein, 1997; Klein & Baxter, 2009).
Cognitive Flexibility Theory is designed for learning in complex knowledge domains. Hence, where there are concepts interacting with high variability, and the need to handle constant novelty. In this theory, authors states that to be able to apply this knowledge from formal instruction to real world cases (which are complex and dynamic), the knowledge must be learnt flexibly. To achieve this goal, there are key principles to respect.
Let’s see how SkillGym applies these aspects:
- Real-world complexity: SkillGym avoids oversimplification by using digital role-plays that mirror real-life situations, including dynamic scenarios and lasting consequences of decisions.
- Case-based learning: The method emphasizes diverse, context-rich examples through a wide range of scenarios, allowing learners to experience skills in various contexts.
- Multiple representations: SkillGym offers different perspectives on the same skills or tasks through its diverse library and expert-created content.
- Interconnected knowledge: The use of Circuits (sets of related scenarios) and Programs (sequences of Circuits) helps learners see connections between concepts and avoid compartmentalization.
- Adaptive knowledge application: By practicing skills across various scenarios, learners develop the ability to flexibly apply their knowledge to new situations.
- Active knowledge construction: The dynamic nature of the role-plays encourages learners to actively build understanding rather than just memorize facts.
Those principles explain where the SkillGym method’s strength lies, and why it is so effective in enabling learners to develop deep, flexible knowledge that can be directly applied in real-world situations.
The importance of feedback
“Learning Must Involve Unlearning”
When someone learns from experience in real-world situations, they need the essential ability to reflect on their own performance—understanding what led to success or failure and why.
Cognitive Transformation Theory (CTT) states that people can revise their belief systems and mental models through experience, particularly when those models prove inadequate. So, thanks to experience people can extend, adjust, reject existing mental models in a continuous process of elaboration and replacement. Therefore, learning also involves “unlearning” and replacement.
In real-world environments, this process takes a considerable amount of time. What if you could speed up this process by providing effective feedback? One way to make this happen is through the “sensemaking”. Sensemaking can be defined as “how people make sense out of their experience in the world”(Klein et al., 2006). It is relevant in Virtual Environment (VE) to help trainees to build more robust mental models (Klein & Baxter, 2009).
Consistently with this theory, SkillGym has a powerful s Sensemaking. Those familiar with SkillGym already know that a significant part of the method is accounted for by what happens after the role-play. After the lifelike interaction, the trainee encounters different types of feedback:
- Eavesdrop feedback: emotional feedback
- Augmented Replay: qualitative feedback
- Analytics: quantitative feedback
The method is built upon a circular interaction that has a clear direction and specific patterns: preparation for the meeting, guided lifelike interaction, self-assessment, emotional feedback from the character, analytical feedback, and numerical feedback. We believe that Sensemaking is, indeed, one of SkillGym’s strengths. The Sensemaking guides the trainee in the understanding of the experience made by the practice during the simulation.
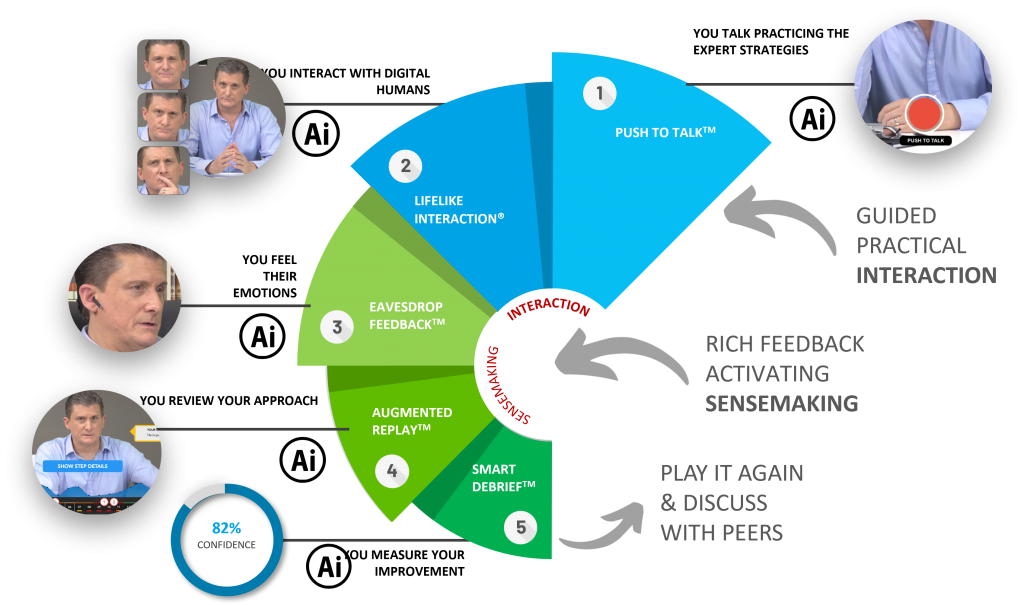
We believe this approach helps trainees maximize their results. They can practice and reflect on their experiences through sensemaking and feedback, and repeat this process, applying new conceptualizations and reinforcing the cognitive abilities just acquired.
How SkillGym works on Minds
What is the mechanism that allows the skills trained by SkillGym to transfer to real-life situations?
Once again, the answer lies in cognitive psychology, particularly Transfer Appropriate Processing (TAP) theory. Developed through over twenty years of research, TAP theory proposes that training is most effective when it recreates the mental processes used in real situations.
While training environments don’t need to perfectly mirror real-world settings, they must engage the same cognitive elements. The key is reinstating specific experiences and practicing critical skills.
We claim that SkillGym allows to synchronize the processes engaged during the simulation and the ones engaged during the real-life performance, and it does it from two different perspective.
SkillGym achieves this synchronization from both: cognitive and emotional perspective.
This approach ensures the validity of the experience, preparing trainees for the full spectrum of challenges they may face in actual situations. By providing a psychologically safe environment for practicing critical scenarios, SkillGym enables a highly effective skill transfer to real-world situation.
Conclusion
SkillGym is a training method rooted in cognitive science, particularly Cognitive Flexibility Theory and Cognitive Transformation Theory. It accelerates expertise development in complex domains through:
- Expert task analysis to transfer the mental model
- Case-based scenarios
- Hint-driven practice
- Targeted feedback
- Engaging motivational strategies
By aligning training processes with real-world scenarios, SkillGym maximizes skill transfer, making it a powerful tool for developing complex decision-making and interpersonal skills.
If you want to get deeper
Crandall, B., Klein, G., & Hoffman, R. (2006). Working Minds: A Practitioner’s Guide to Cognitive Task Analysis. https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/7304.001.0001
Hoffman, R. R., Ward, P., Feltovich, P. J., DiBello, L., Fiore, S. M., & Andrews, D. H. (2013). Accelerated expertise: Training for high proficiency in a complex world. Psychology press.
Klein, G., & Militello, L. (2001). Some guidelines for conducting a cognitive task analysis. In Advances in Human Performance and Cognitive Engineering Research (Vol. 1). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1479-3601(01)01006-2
Klein, G., & Baxter, H. C. (2009). Cognitive transformation theory: Contrasting cognitive and behavioral learning. The PSI Handbook of Virtual Environments for Training and Education: Developments for the Military and beyond, Vol. 1: Learning, Requirements, and Metrics, November, 50–65.
Spiro, R., Coulson, R., Feltovich, P., & Anderson, D. (2013). Cognitive Flexibility Theory: Advanced Knowledge Acquisition in Ill-Structured Domains. In Theoretical Models and Processes of Reading (pp. 544–557). https://doi.org/10.1598/0710.22